Abstract
Background: Chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy is known to produce durable remissions in the treatment of CD19 + relapsed/refractory B cell malignancies. Nonetheless, many patients receiving CAR-T cells will fail to respond for unknown reasons. Here, we employed single cell RNA sequencing and protein surface marker profiling of serial CAR-T cell samples from patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) to reveal CAR-T cell evolution, identify biomarkers of response, and test for evidence of exhaustion in CAR-T cells of poor responders.
Methods: To describe the evolution of CAR-T cells after infusion into NHL patients and to identify mechanisms and biomarkers of response, our study examined manufactured CAR-T cell products and FACS isolated CAR-T cells from post-infusion blood samples from patients treated for CD19 + relapsed/refractory NHL. Utilizing scRNA sequencing and flow cytometry, we investigated time points after infusion that are known from previous studies to be associated with peak expansion (day 14) and contraction (day 30) and represent key changes in CAR-T cell activity. Altogether, our datasets include 14 manufactured CAR-T cell products, 13 samples from day 14, and 12 samples from day 30. This sampling represents 10 patients with favorable response (complete or partial remission (CR; PR)) and 4 patients with poor response (stable or progressive disease (SD; PD)).
To isolate CAR-T cells for scRNA sequencing, viable CD3 +CAR + cells were sorted from cryopreserved CAR-T cell products or PBMCs. Next, libraries were generated with the 10x Genomics Chromium single cell 3' platform with feature barcoding technology to allow simultaneous and paired quantification of transcriptional and cell surface protein expression in individual CAR-T cells. The libraries were sequenced and the data stringently filtered. Batch effect removal was applied to remove differences due to sample preparation or sequencing.
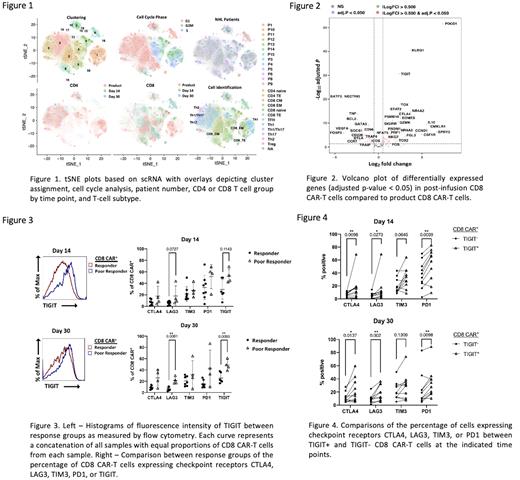
Results: Post-filtering, our dataset contained 94,000 cells with an average of 3,917 cells per sample, 8,518 reads per cell, and 2263 unique detectable genes per cell. After dimension reduction and clustering, eleven high-frequency clusters were identified with cluster patterns corresponding with time point, cell cycle phase, cell type, or patient (Figure 1).
At the transcriptional level, post-infusion CD8 CAR-T cells displayed significant upregulation of transcription factors (PRDM1, EOMES) and cytotoxic effector molecules (GZMB, PRF1, GZMK, CCL5) associated with differentiation into cytotoxic effector cells as well as transcription factors associated with exhaustion (TOX, TOX2, NR4A2, NR4A3) (p.adj < 0.05) (Figure 2). These data were corroborated by enrichment of effector and exhaustion gene set signatures after infusion as well as global increases in the protein expression of activation and exhaustion markers CD45RO, CD69, CD57, PD1 (CD279), and TIGIT.
Contrasts of CAR-T cells between response groups displayed enrichment of an exhaustion profile in CD8 CAR-T cells of poor responders characterized by significant upregulation of the transcription factors FOS, JUNB, JUND, FOSB, JUN, NR4A2, NFKBIA, and PRDM1 and other markers of exhaustion at the RNA level (p.adj < 0.0001). At the protein level, the frequency of TIGIT expression was 20% greater on average in the CD8 CAR-T cells of poor responders compared to favorable responders (Figure 3). CD8 CAR-T cells expressing TIGIT compared to TIGIT negative CD8 CAR-T cells were enriched in an exhaustion transcriptional profile by gene set enrichment analysis and expressed consistently higher levels of exhaustion markers (PD1, CTLA4, LAG3, TIM3) by flow cytometry, regardless of response group or time point (Figure 4).
Conclusions: At the transcriptional and protein levels, we note the evolution of CAR-T cells toward a non-proliferative, highly-differentiated, and exhausted state that is enriched in CAR-T cells of patients with poor response. Furthermore, we identified the checkpoint receptor TIGIT as a novel prognostic biomarker and potential driver of CAR-T cell exhaustion.
Dropulic: Lentigen: Ended employment in the past 24 months, Patents & Royalties. Caimi: Kite Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; XaTek: Patents & Royalties: Royalties from patents (wife); Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Genentech: Research Funding; ADC Theraputics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Verastem: Consultancy; Amgen Therapeutics.: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria. de Lima: Miltenyi Biotec: Research Funding; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.